-
-

Please Wait...
-
.net.cn Chinese Domain Country Information - .net.cn China Country Information
.net.cn

Price and Requirements for .net.cn Domains
Registration Pricing
- 1 Year 29.99 USD
- 2 Years 58.78 USD
- 3 Years 87.27 USD
- 4 Years 115.16 USD
- 5 Years 142.45 USD
- 6 Years 169.14 USD
- 7 Years 195.23 USD
- 8 Years 220.73 USD
- 9 Years 245.62 USD
- 10 Years 269.91 USD
Application Fee
19.92 USD
Registration Time Frame
1 Day
Requirements
Yes Details Are Individual .net.cn domain registrations allowed?
Yes Details Company or legal entities registrations allowed for .net.cn?
Yes Details Are there requirements, documents, or information needed for .net.cn?
Yes Details Are some .net.cn domain names restricted?
No Details Does .net.cn domain have a special use?
Yes Details Other information I need to know about .net.cn?
Yes Details Are there any additional fees for .net.cn?
No Details Do I need a trademark/brand name to register .net.cn?
No Details WHOIS Privacy service available?
![]() Trustee / Proxy service offered? Fees?
Yes
Details
Trustee / Proxy service offered? Fees?
Yes
Details
.net.cn China Country Information
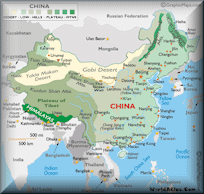
The People's Republic of China is a single-party state governed by the Communist Party of China. It exercises jurisdiction over 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four directly controlled municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing), and two mostly self-governing special administrative regions (SARs), Hong Kong and Macau. Its capital city is Beijing. The PRC also claims the island of Taiwan, which is controlled by the government of the Republic of China, as its 23rd province, a claim controversial due to the complex political status of Taiwan and the unresolved Chinese Civil War.
China’s landscape is vast and diverse, with forest steppes and the Gobi and Taklamakan deserts occupying the arid north and northwest near Mongolia and Central Asia, and subtropical forests being prevalent in the wetter south near Southeast Asia. The terrain of western China is rugged and elevated, with the Himalaya, Karakoram, Pamir and Tian Shan mountain ranges separating China from South and Central Asia. The world’s apex, Mt. Everest (8,848 m), lies on the China-Nepal border, while the world's second-highest point, K2 (8,611 m), is situated on China's border with Pakistan. The country’s lowest and the world’s third-lowest point, Lake Ayding (-154 m), is located in the Turpan Depression. The Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, the third- and sixth-longest in the world, have their sources in the Tibetan Plateau and continue to the densely populated eastern seaboard. China’s coastline along the Pacific Ocean is 14,500 kilometres (9,000 mi) long (the 11th-longest in the world), and is bounded by the Bohai, Yellow, East and South China Seas.
The ancient Chinese civilization—one of the world's earliest—flourished in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. China's political system was based on hereditary monarchies, known as dynasties, beginning with the semi-mythological Xia of the Yellow River basin (approx. 2000 BC) and ending with the fall of the Qing Dynasty in 1912. Since 221 BC, when the Qin Dynasty first conquered several states to form a Chinese empire, the country has fractured and been reformed numerous times. The Republic of China (ROC), founded in 1912 after the overthrow of the Qing dynasty, ruled the Chinese mainland until 1949. In the 1946–1949 phase of the Chinese Civil War, the Chinese Communists defeated the Chinese Nationalists (Kuomintang) on the mainland and established the People's Republic of China in Beijing on 1 October 1949. The Kuomintang relocated the ROC government to Taiwan, establishing its capital in Taipei. The ROC's jurisdiction is now limited to Taiwan and several outlying islands, including Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu. Since 1949, the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China (now widely known as "Taiwan") have remained in dispute over the sovereignty of China and the political status of Taiwan, mutually claiming each other's territory and competing for international diplomatic recognition. In 1971, the PRC gained admission to United Nations and took the Chinese seat as a permanent member of the U.N. Security Council. China is also a member of numerous formal and informal multilateral organizations, including the WTO, APEC, BRICS, the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and the G-20. As of September 2011, all but 23 countries have recognized the PRC as the sole legitimate government of China.
Since the introduction of market-based economic reforms in 1978, China has become the world's fastest-growing major economy, and the world's largest exporter and second-largest importer of goods. It is the world's second-largest economy, after the United States, by both nominal GDP and purchasing power parity (PPP). On per capita terms, China ranked 90th by nominal GDP and 91st by GDP (PPP) in 2011, according to the IMF. China is a recognized nuclear weapons state and has the world's largest standing army, with the second-largest defense budget. In 2003, China became the third nation in the world, after the former Soviet Union and the United States, to independently launch a successful manned space mission. China has been characterized as a potential superpower by a number of academics, military analysts, and public policy and economics analysts.
The territory of China lies between latitudes 18° and 54° N, and longitudes 73° and 135° E. The country's vast size gives it a wide variety of landscapes. In the east, along the shores of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea, there are extensive and densely populated alluvial plains, while on the edges of the Inner Mongolian plateau in the north, broad grasslands are visible. Southern China is dominated by hill country and low mountain ranges, while the central-east hosts the deltas of China's two major rivers, the Yellow River and the Yangtze River. Other major rivers include the Xi, Mekong, Brahmaputra and Amur. To the west, major mountain ranges, most notably the Himalayas, and high plateaus feature among the more arid landscapes of the north, such as the Taklamakan and the Gobi Desert. China's highest point, Mt. Everest (8848m), lies on the Sino-Nepalese border. The country's lowest point is the dried lake bed of Ayding Lake (-154m) in the Turpan Depression.
A major environmental issue in China is the continued expansion of its deserts, particularly the Gobi Desert, which is currently the world's fifth-largest desert.[90][91] Although barrier tree lines planted since the 1970s have reduced the frequency of sandstorms, prolonged drought and poor agricultural practices have resulted in dust storms plaguing northern China each spring, which then spread to other parts of East Asia, including Korea and Japan. According to China's environmental watchdog, Sepa, China is losing a million acres (4,000 km²) per year to desertification. Water quality, erosion, and pollution control have become important issues in China's relations with other countries. Melting glaciers in the Himalayas could potentially lead to water shortages for hundreds of millions of people.
.net.cn China Domain Name - Country Information
| Country Domain | China Domain Name .net.cn |
|---|---|
| Country Information | China Domain Country Information .net.cn |
| TLD Bulk & Advanced Search | China Bulk Domain Registration .net.cn |
| WhoIs Server | .net.cn Whois Server Information |
| Domain Renewals | Renewal Chinese Domain .net.cn |
| Domain Transfer | Transfer Domain .net.cn |
| Domain Hosting | .net.cn China Web Hosting |
| SSL Certificates | SSL Certificates |
| Email Services | .net.cn China Email Services |
| Domain FAQ | .net.cn Domain Registration FAQ |
China Country Information Search Terms
Chinese Domain Country Information Chinese Domain Registrar Chinese World Wide Domain Registration Chinese Country Code Top Level Domain .net.cn Domain Information Chinese Country Information China Country Information